
Now that you have set up your shop, you need customers visiting your shop to buy things. But how are you going to get the word out?
You basically have 3 options; you can do pay per click advertising, other types of paid ad placements, or organic SEO. Organic SEO is by far the best option to use, but it does not work overnight.
What is Organic SEO?
You might have heard people use the term organic SEO but do you actually know what it means? Organic SEO is the term used to describe the ranking that search engines naturally give your site without using any kind of paid advertising. Searches have a tightly guarded metric used for determining a sites rank in the Search Engine Results Pages (this is also called the SERP’s). Google uses over 200 different metrics to determine a sites placement; Bing has around the same number of metrics (did you know that Yahoo’s search results are actually provided by Bing).
Where to start?
In this article, I assume you have a basic knowledge of Prestashop. This article will rely solely on the features built into Prestashop without using any outside modules. I will try to explain everything as in-depth as possible so that you get a clear understanding of what you are doing and why you are doing it. Now, log into your back office and let’s get started.
The first thing you want to do is turn on your friendly URLs for your site. In your back office go to Preferences » SEO and URLs. The page will look like the image below.
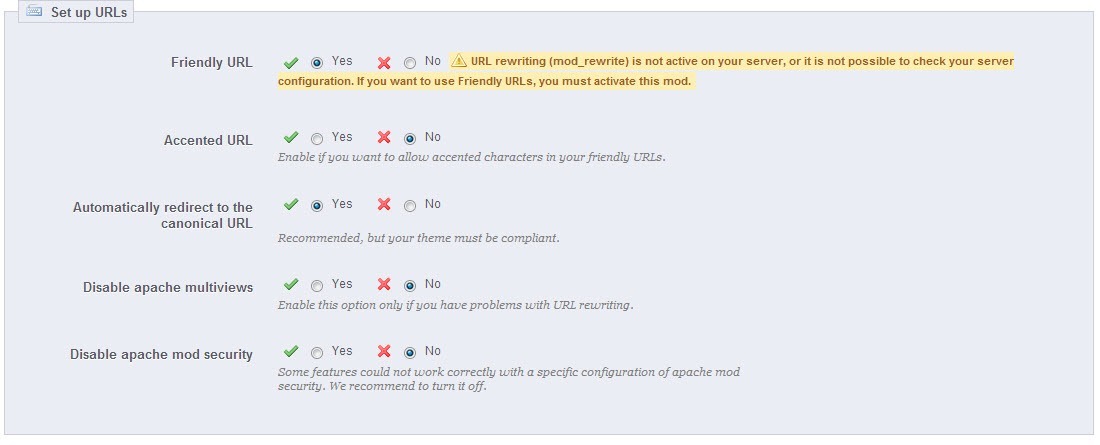
Click the radio button next to Friendly URL and the one next to automatically redirect to the canonical URL. Once you select those, press save. If you notice in the image above there is a warning message on the Friendly URL. This sometimes happens because of the way that your server is set up. If you press save and then your site becomes inaccessible it means that mod_rewrite is not active on your server. You should contact your host and have them install or enable it; it is very important to the SEO of your website. To fix your site in the meantime, you will have to ftp into your site and delete the .htaccess file. Then go back to the SEO and URLs page and turn off Friendly URLs and the automatically redirect to canonical URL. In this example, the warning message goes off but it is a false alarm and nothing to worry about, this sometimes happens.
Friendly URLs are very important for the SEO of your site. Below is a graphic from SEO Moz about the structure of URLs.
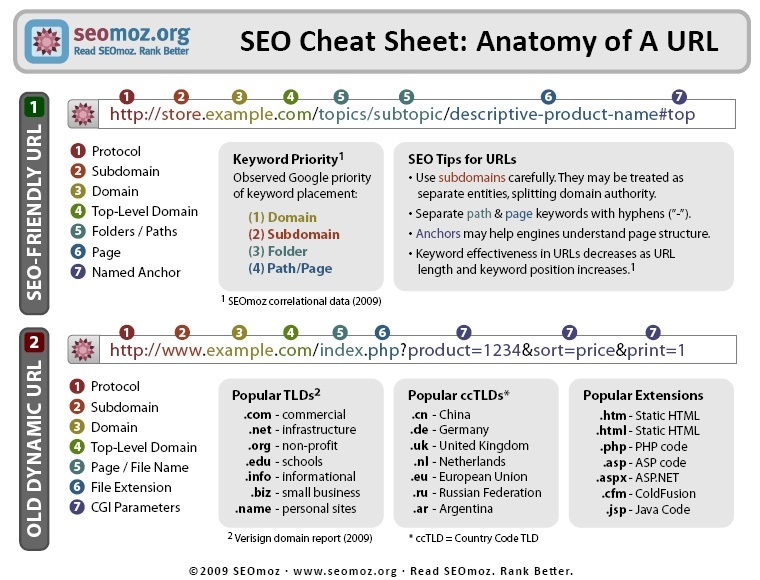
Now, let’s look at an example from Prestashop and dissect it.
This is an standard dynamic URL that Prestashop uses before you turn friendly URLs on. This is for the test product “Belkin Ipod Case.”
http://site.com/index.php?id_product=6&controller=product
This is the friendly URL version
http://site.com/accessories-ipod/6-belkin-leather-folio-for-ipod-nano-black-chocolate.html
By looking at the unfriendly URL, you or search engines have no idea what is on the actual page but by looking at the friendly URL, you have a pretty good idea what you are going to be looking at. Search engines are like people in a lot of rights because search engines look at the URL to determine how relevant the page is to a search result.
The friendly URL in the example is not concise. You want to use the fewest amount of words to describe the product. A better URL would be “http://site.com/accessories-ipod/6-belkin-leather-ipod-nano.html” The reason being is every word after the top level domain is given an equal weight. The fewer the words in a URL the more weight each word carries with the search engines.
The canonical URL and its place in SEO is tricky to understand. Search engines use a system called page rank. Google updates its main page rank database every 3 months or so and so does Bing. The higher page rank a page has, the more likely it will be shown versus other pages in the SERP’s. Page rank is generally on a scale of 0-10. There is also a N/A rating, meaning the page has not been assigned a rank yet. Sites like Facebook and Twitter are 10’s because of popularity and the high volume of traffic. The reason why I am explaining page rank, is because it can be split between the same page in a not so good manner. For example take a look at the 4 URLs below.
http://site.com
http://site.com/
http://www.site.com
http://www.site.com/
Usually all 4 of those URLs will take you to the same page. The canonical redirect makes sure that when you go to any of those 4 URLs, the address in the address bar is redirected to the correct address. This makes sure that your page authority is not split over those 4 URLs and makes all of the authority go to one URL, which gives your shop a better ranking over time.
On to Meta information
Meta information, also called meta tags, are little snippets of information that are not shown on the page. Search engines use it to classify pages of a site and use it as one of their indicators to judge what the page is about. Meta information is separated into 3 parts.
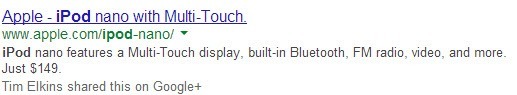
| Title – This is the title of the page and the description shown in the top of the browser bar. Your meta title needs to be about 70 characters and as few words as possible. Every word in the title is given a weight. The more words, the less weight that each word carries. Also remember that Prestashop adds the shop name to the end of your title, so take that into account when you come up with your title. One other thing to keep in mind, most of the time titles are the main snippets used to describe the page in the search engine. For example in the image below the page title is “Apple – Ipod nano with Multi-Touch”. Be concise and to the point with these tags, it will be the first thing people see coming from a search engine. You want to make the titles appealing so people will click them. You can also use either | or – to separate words or phrases in your titles. |
Meta Description – The meta description is the description directly under the title in the SERP’s. You want to limit it to around 155 characters or it will get truncated in search engines. The best thing you can do with this text is make it readable and as descriptive as possible. Do not use it to just stuff keywords in; search engines are wise to that. Other things to keep in mind are to always write compelling copy and use a different meta description for every page as the meta description does not actually factor into the ranking of the pages anymore.
Meta Keywords – The meta keywords tag is a touchy subject with a lot of people. Google has confirmed that it no longer uses meta keywords in any way to rank a web page. Bing, however, has been very mysterious about how they use the meta keyword tag. So my suggestion is to only use about 2-3 words per page, if you use them at all.
Friendly URL – The friendly URL is the URL that Prestashop will write after the site name or site name and category name if you are on a product page. Treat the friendly URL like the page title. I would suggest using the same thing as the page title as it makes the page more relevant for those search terms.
Now that you have a little information about each tag and what their purpose is, you can start adjusting them. When you go to Preferences » SEO and URLs, the list at the top of the page is all of the default pages that Prestashop creates for the site to run smoothly. See the image below.
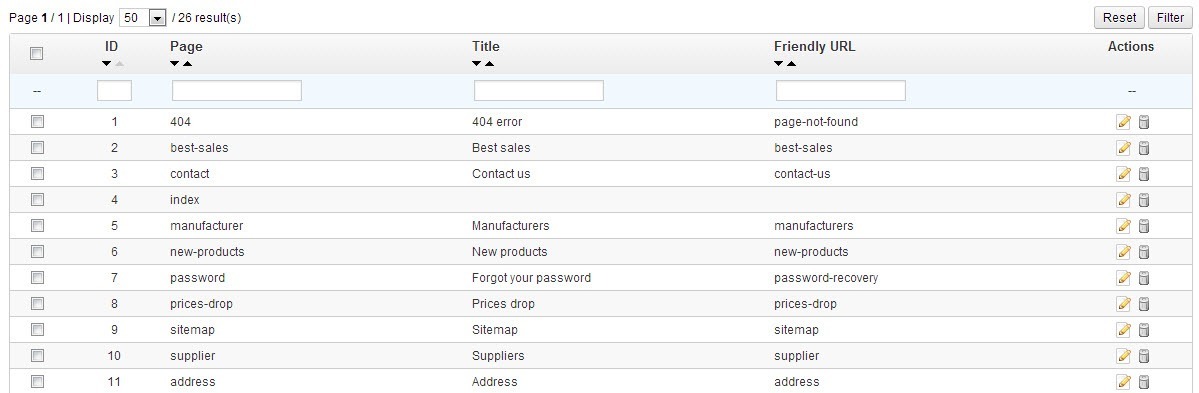
If you click the pencil and paper icon to the right of the page name, then you can set the meta tags for each page. I suggest changing these since every Prestashop installation has the exact same text. Keep in mind that some of these pages are blocked from search engines indexing them; we will talk more about that later. When you click the pencil and paper icon on the right, the page will look like the image below.
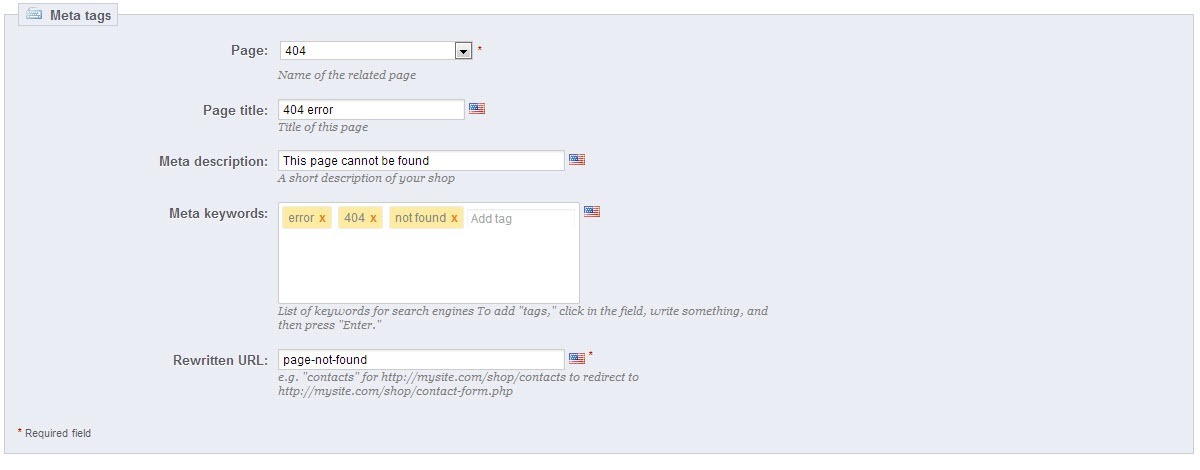
Once you change the information to what you want to use, press save at the top of the screen and move on to the next page.
CMS and Category Pages
The CMS pages are laid out the same way as the meta descriptions. To access your CMS pages go to Preferences » CMS. Once you are there, click on the pencil and paper icon like you did with the pages that Prestashop creates.
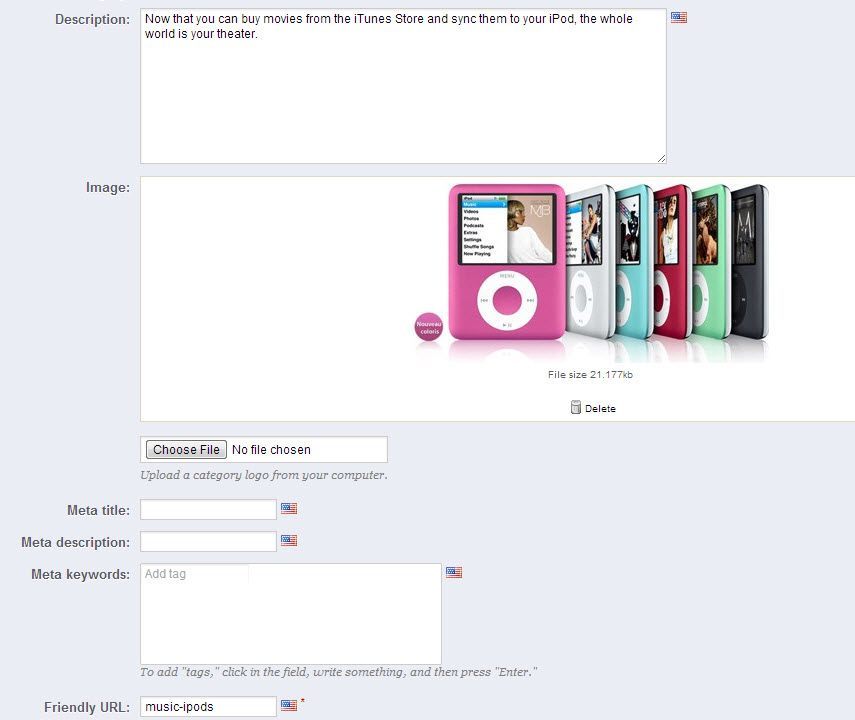
To edit the categories, it is the same process, go to Catalog » Categories and click the pencil and paper icon to edit them. The categories have a couple of extra fields that the other pages do not have. You can write an on-page description for the categories and you can also upload an image for the categories. Using these depends on your theme, how it is laid out, and if it looks good having them. I would suggest at least using the description to provide a little bit of information about the category. See the image below.
Product Page SEO Information
The product pages are laid out a little bit differently than the other pages. Inside the product page there is an SEO tab. It looks like the image below.
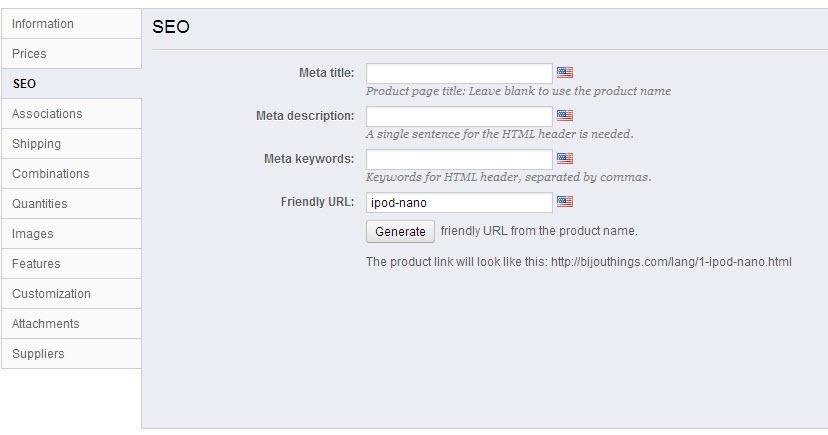
In this tab you can enter the same information that you would in the other sections.
Apart from using the meta data on the product pages, I would suggest writing good descriptions. Well written descriptions help a site rank higher, especially if you are using a data feed. If you are using a data feed, then everyone else in the world that is using the same feed is using the same descriptions. So what makes you think that your site is going to rank higher than theirs? Having clear, to the point descriptions that reference what the page is about a few times are good. I would make the long description at least 500 characters, if you can. Also, use the features to list the different features of the product. This is helpful to the customer, especially if they are looking for a product with a specific feature. Great descriptions go a long way in giving customers confidence in a site and selling your products.
One other note, if your products have a unique number to identify them such as a bar code, UPC, or EAN 13, fill those out. When people search for the lowest price on a specific product, they often times only search by that number.
That concludes this lesson.
In the next article, I will show you how to set up your Google analytic’s account, your Google web master account, and your Bing account.
About the Author: Lesley Paone
Lesley has worked in e-commerce for over a decade, and is the founder of dh42. Starting out with PrestaShop and brancing out into other platforms like Shopify. He loves all things e-commerce and loves a challenge, in his spare time he helps moderate several forums on SEO, e-commerce, as well as the PrestaShop forum. If you have any questions for him about any of his articles just use our contact form to contact him.
